Disability generally affects everyone, both people with disabilities and those taking care of people with disabilities in almost every sector of their everyday life, depending on the severity of the Disability.
To know how much Disability has affected Aussies, we need to check on the research reports done by the Australian Bureau of Statistics in 2023.
Here is what was reported;
- Over 50% of senior citizens over 85 years are living with a disability
- In the next few years, more than 4 million Aussies will be dealing with a disability
- The number of disability cases will rise between 2023- 2030 as the current citizen’s age
How Many Kinds Of Disabilities Are There?
There are an uncountable number of disabilities that can affect people, with some being a bit more common and more sensitive than others.
As a result, Australia’s government acknowledges those sensitive and offers financial support to people with disabilities and their families.
Twenty-one kinds of disabilities affect more people than others, and the government offers support to them; each government has identified its own set of protocols they use to offer support.
1. Blindness
Blindness is also known as sightlessness, where the person can not see either wholly or partially. However, the blindness that the government supports is where the person cannot see, the case where they cannot note the difference between day and night from both eyes.

2. Low-visibility
Low vision means that the individual is dealing with either of the following conditions;
- The visual acuity does not go beyond 6/18 or is below 20/60 up to 3/60 or 10/200 in the good eye after the best possible treatment.
- Vision limitation binding 10 degrees up to 40 degrees( does not go beyond 40 degrees)
3. People Recovering From Leprosy
Leprosy is a chronic and highly infectious bacterial disease caused by the orgasms of Mycobacterium Leprae. Also called Hansen’s disease (HD), leprosy often targets the skin, mucosal surfaces, peripheral nerves, the eyes, and the upper respiratory tract.
Although most believe it existed long ago, leprosy is still a common disease affecting young children and very older adults. However, not everyone who contacts Laprea bacteria catches the disease- it mostly goes away on its own

4. Hearing Impairment
Hearing impairment comes in two ways; partial or difficulty in hearing and deafness.
When someone is pronounced deaf, they have a 70dB loss in the hearing ability for both ears, while hard of hearing means the loss is between 60dB to 70dB in both ears.
5. Mobility Disability
People with Locomotor disabilities commonly face difficulty moving their bodies or handling objects. Such problems may arise from injury to the nervous and musculoskeletal systems.
Mobility disability is an illness related to the joints, bones, and muscles, which brings about motion problems walking or even picking a spoon.
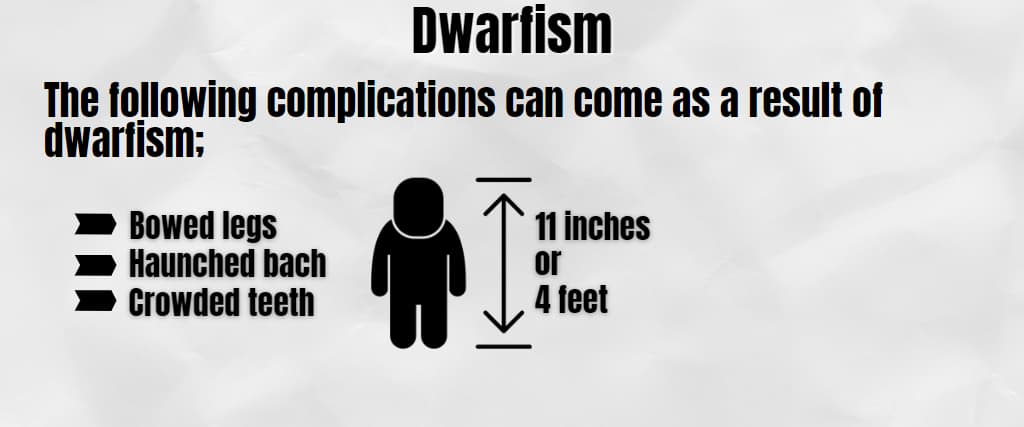
6. Dwarfism
Restricted growth is a form of mutation that affects the growth of bones, which means that an adult person will be about 11 inches and below, which equates to about 4 feet. The following complications can come as a result of dwarfism;
- Bowed legs
- Haunched bach
- Crowded teeth
However, the most common way to identify dwarfism is by noting shorter-than-ideal height,
7. Actual Learning Disability
Mental retardation is a condition characterised by notable intellectual dysfunction, including limitations in problem-solving skills, learning, reasoning, and challenges adapting to a new environment.
These can be seen from how they relate with others, among other practical skills; it can also be called mental retardation or general learning disability.
8. Mental Disorder
Mental illness is an extreme disorder of perception, thinking orientation, moods, behaviour, and memory that unacceptably alters judgment. It is the inability to differentiate reality and illusion and the failure to meet basic living standards.
However, mental illness is different from retardation in that retardation is characterised by difficulty in reasoning and thinking due to incomplete mind development, while mental disorders mainly affect thinking moods and behaviour
9. Autism Spectrum Disorder
Ideally, most people are diagnosed with autism before they reach two years, although it can still be caught later- especially the mild cases of autism.
It is a development and neurological disorder that alters mainly the behaviour and communication of a person. Autism targets an individual’s entire emotional, physical, social, and cognitive system.
It requires a clinical diagnosis and, in most cases, cannot be cured; the effects of autism are managed with medication
10. Cerebral Palsy
The cerebral condition results from brain damage and affects children before childbirth, so they cannot fully coordinate their muscles.
Unlike most other illnesses, cerebral palsy does not typically worsen over time, even without medication. However, the severity of the disabilities associated with the condition may increase as time passes.
Cerebral palsy is incurable, but there are medications to slow down the progress of the disabilities caused by the disease
11. Muscular Dystrophy
It is a series of more than 35 genetic illnesses characterised by progressive general weakness and deterioration of the voluntary muscles used when voluntarily moving around.
These disorders can vary in when they occur and in muscle patterns. As soon as the patient has been diagnosed, they need to be put on immediate medication to slow down the progression of the disease.
12. incurable Neurological Conditions
Here is a list of incurable neural diseases;
- Dystonia
- Neuromuscular illness
- Stroke
- Huntington’s condition
- Epilepsy
- Lou Gehrig’s disease- ALS
- Cerebral palsy
- Dementia and Alzheimer’sAlzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
13. Specific Learning Deficit
It is a series of several disabilities that alter someone’s ability to think, listen, speak, spell, write, and handle simple mathematical calculations.
Two or more of these listed abilities may be fettered when someone has a specific learning deficit disease.
14. Multiple Cerebral Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis, or disseminated sclerosis or encephalomyelitis disseminata, is a disease characterised by the immune system attacking the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord.
When the attack happens, the medullary sheath gets damaged and causes complications with how information goes through the nervous system. The condition can cause complete nerve damage in the long run if left untreated.
15. Language Disorders
Language disability is a permanent disorder where the patient has trouble combining words needed to complete a sentence, which makes it rather hard to understand or communicate with them.
It comes from problems like aphasia or laryngectomy that affect speech components due to neurological issues. Most of these disorders are generally phonological and articulation disorders.
16. Thalassemia
Thalassemia, which characterises itself as fatigue or general body weakness, slow growth, and paleness, is an inherited blood disease that affects the production of hemoglobin.
The body produces abnormal or less hemoglobin due to the massive destruction of the red blood cells, which causes anemia. Hemoglobin is a protein in the red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen in the various body parts.

17. Factor VIII Deficiency
It is a blood complication caused by a lack of clotting proteins in the blood, leading to prolonged bleeding when an injury occurs. Hemophilia is more common in men than women; boys inherit it from their mothers. The most common symptoms are:
- Joint swelling
- Joint pain
- Blood in stool or urine
- Unexplained bleeding
- Many severe bruises
18. Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell disease affects the red blood cells by causing them to appear sickled, distorted, and eventually break down, drastically reducing their capacity to carry blood to the entire body.
It is a genetic disease characterised by malaise, rapid chest pain, fatigue, low oxygen levels, and anemia.
19. Multihandicapped, Including Blindness and Deafness
Multiple Disability occurs when the patient has two or more disabilities affecting their daily activities. There is no specific sequence to this occurrence; they can affect the motor and the sensory body parts or simply motor parts.
20. Acid Attack Victims
Acid attack victims are people whose faces and other parts of the body have been disfigured after being attacked with corrosive substances like acids
21. Primary Parkinsonism
Also known as idiopathic parkinsonism or paralysis agitans, Parkinson’s disease is a disorder that attacks the central nervous system affecting the body’s movement.
The most common symptoms are:
- tremors
- slowed movement
- Tremor
- stiffness
- imbalance of the motor system
Currently, there is no cure for the disease, just medications to slow down the symptoms that worsen over time; it is rapidly progressive.
Analytical Analysis
The Australian Network, in conjunction with the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare on disabilities, did research on disabilities and came up with the following results:
Population Tally:
- Among the people living with disabilities, about 50% of them were over 65 years- about 1.9 million people.
- More than 2.1 million Aussies aged 15-64( working age) were people with disabilities.
- About 9 million households(36) have a member living with Disability.
Different Kinds of Disabilities
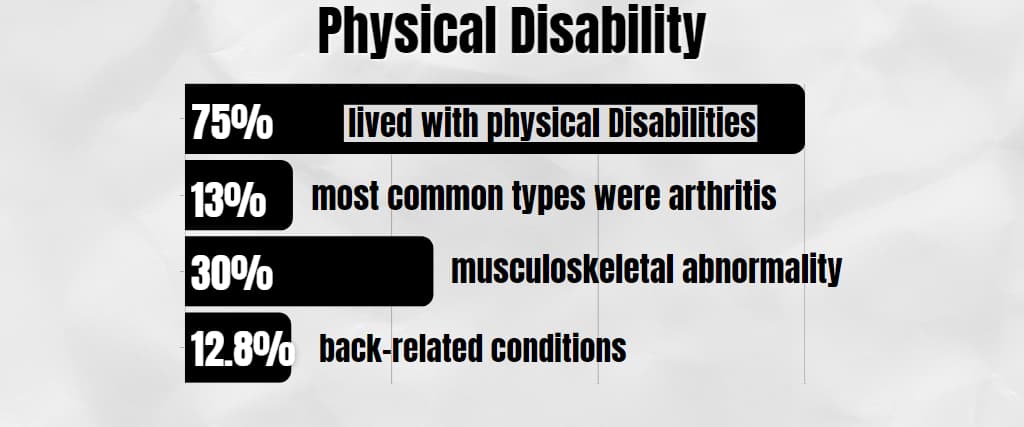
Physical Disability
Out of the entire population of disabled people, more than 75% lived with physical Disabilities. The most common types were arthritis (13%), musculoskeletal abnormality (30%), and back-related conditions (12.8%)
Mental Disorders
More than 40% of citizens from 17 to 84 years have dealt with a mental disorder at a specific time in life.
From a study conducted by Vision Australia, there are about 360,000 people in Australia living with either permanent or partial blindness. However, medical researchers expect that the number will double by 2030.
Impairment in Workplaces
In Australia, the percentage of disabled people employed both in the formal and informal sectors is about 48%, which is relatively low compared to the employment rate of those without disabilities, which is about 80%.
Moreover, approximately 1 in 5 individuals with disabilities have encountered discrimination in the workplace, primarily from their employers but also from their colleagues.

Impairment From Client Service
1 out of 3 people living with disabilities often complain of poor customer service, where their complaints are often unmet.
Compared to people living without disabilities, 36% per cent of people living with disabilities are often discriminated against, even in service areas like restaurants or malls.
To Note
Impairments
- In 2018, the number of people living with disabilities was 4.4 million and represented about 17.7% of the population; the number reduced from 17.7% in 2015.
- The older people got, the more their chances of living with disabilities increased; 11% of the people living with disabilities were between 0-65, while 49.6% were above 65 years.
- There wasn’t much distinction in terms of disability both in males and females; (17.6% and 17.8%, respectively)
- 5.8% of the citizens were living with chronic disorders
- 24% of the people living with disabilities were dealing with both behavioural and mental problems as their main symptoms; the number was a rise by 2% from 2015
Those Living With Disabilities at Home
- 34% of those above 15 years had finished year 12, which was an improvement of 2% from 2015
- 16% of citizens living with disabilities had a bachelor’s degree, which was a rise of 1.2% since 2015
- 38% of disabled people between 15-64 years depended on government pensions or allowances as their source of income, which dropped from 42% in 2015
- About 60% of the people living with disabilities had people to take care of them- the number dropped from 62% in 2015
- Around 10% of individuals with disabilities have faced discrimination based on their impairments within the last year. This figure represents an increase from the 8.5% reported in 2015.
- The employment rate for individuals with disabilities has remained stable since 2015, while the rate for those without disabilities has increased by approximately 4%.
- 12% of the people living with chronic disabilities between 15-64 years had full-time jobs, which was a rise of 3% since 2015
Senior Citizens
- 3.9 million people living with disabilities in Australia were above 65 years
- Over 95 % of the senior citizens were living with their families, and 5% in nursing homes
- 50% of the senior citizens were living with a disability which is constant from 2015
- 1.3 million senior citizens need help with basic day-to-day activities, and 66% had full support from friends and family. The number was a drop from 70% in 2015
- 68 % of the senior citizens living with disabilities come from low-income families earning below $800 a week
- The majority of the senior citizens were actively helping with household chores.
Helpers
There were 2.7 million helpers(10% of the entire Australian population) which dropped by 1% from 2015:
- 12.4% of the carers were female, while 10.% were men
- The number of helpers below 25 years dropped from 274000 to 235000 since 2015
- 4% of Australians were the primary caregivers
- 0.7 of the caregivers were female
- The number of helpers living with disabilities was 38% which is almost twice the number of those carers without disabilities(14%)
- 70% of the helpers offered to be a carer to honour their responsibilities to their families
- 50% of the carers came from households dealing with low income, while only 25% of the non-caregivers came from low gross income households.
- The number of people living with disabilities has dropped by 1% between 2015-2018. Likewise, the number of people living with disabilities dropped by 0.2% between 2012-2015
How Many Australians Were Living With Disabilities?
The population of people with disabilities keeps rising and is expected to double by 2030. In 2018, the number of people with disabilities was 4.4 million, a rise of 100,000 from 2015.
From the statistics, 2 million were senior citizens exceeding the age of 65; this number also rose by 100,000 since 2015

How Do Sex and Age Affect Disability?
Generally, the older people grew, the more the chances of acquiring a disability increased for both males and females.
Here is a more elaborate statistics
- 3.7% of the population living with disabilities consisted of Children Between 0-4 years
- 87% of the entire population comprised of senior citizens above 90 years
- 12% of children between 5-14 years living with disabilities were female
- 7% of children between 5-14 years living with disabilities were male
Are Disabilities Becoming More Common as the Years Go By?
Between 2015 and 2018, the patterns of disabilities were most common, but with a few differences. Here is what changed in 2018;
- The percentage of disabled people between 60-64 has reduced by 5.6% since 2015( from 31.5%-26.9%)
- The percentage of middle aged people living with disabilities(between 35-44 years) had gone down by 2.2%( from 12.%1-9.9%)
- The percentage of disabled women was 20.5%( between 55-59 years ) as compared to 2015 where they were 24.4( down by 3.9%)
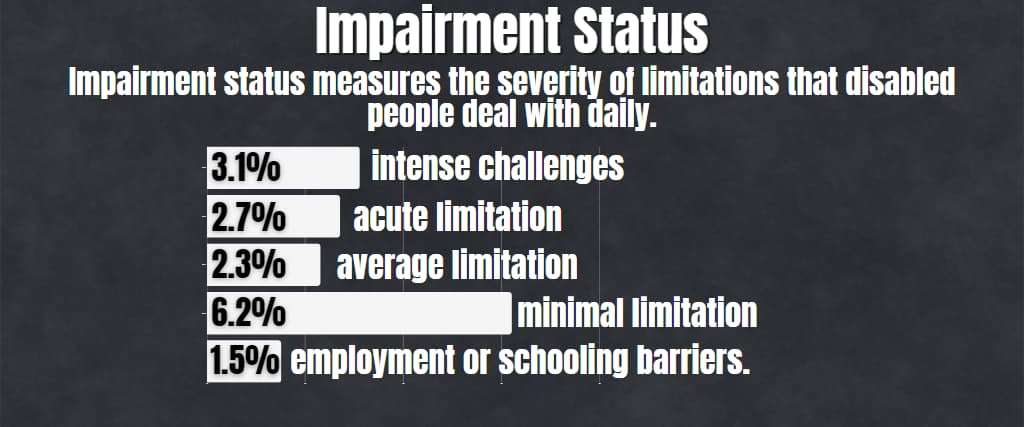
Impairment Status
Impairment status measures the severity of limitations that disabled people deal with daily.
Out of the 4.5 million people living with disabilities in Australia, 3.9 million were dealing with some sort of impairment; mobility, employment challenges, and self-care difficulties.
Here is a more detailed report:
- 3.1% were dealing with intense challenges
- 2.7% were dealing with acute limitation
- 2.3% were dealing with average limitation
- 6.2% were dealing with minimal limitation
- 1.5% were only dealing with employment or schooling barriers.
These were the same rates in 2015

How Do Sex and Age Affect the Severity of Disabilities?
Generally, females(6.0%) have a greater risk of dealing with profound disabilities than men(5.5%). However, in children, boys are more likely to develop complicated disabilities than girls are:
- 1.5% of girls aged 0-4 years compared with 3.3% of boy
- 3.7% of girls aged 5-14 years, compared with 7.5% of boys
Living Conditions
- Most people(95.6%) with disabilities lived with their friends and loved ones; only 4.4 % lived in care homes.
- The older the disabled people get, the more they increase their chances of living in caregiving homes. Additionally, the more severe the disabilities, the higher the chances of being sent to a caregiving home.
- 19% of disabled people over 80 lived in caregiving homes, while only 3% of people between 65-79 lived in houses.
- Only 1% of people living with disabilities were receiving support from caregiving homes.
- 22% of people with extreme complications were living in caregiving homes which is a high percentage as compared to 2.9% who had moderate impairments living in caregiving homes.

How Common Are Disabilities in the USA and Neighbouring States?
Disabilities in the USA and Australia are treated differently due to the difference in age structure between the two countries.
- The leading country in terms of disabilities was Transmania (27%) which was followed by a tie between South Australia and the Australian capital territory (20%)
Additionally, some countries experienced more changes in disability frequency than others between 2015 and 2018
- In South Australia, the number of people living with disabilities dropped from 23% to 19.1%
- In the Australian capital, the number of people with limitations rode from 16.3% to 19.1%
- The number of people living with disabilities in Western Australia rose from 14.5% to 16.3%

What Are the Long-Term Effects of Living With a Disability?
People dealing with severe disabilities are more prone to dealing with mental illnesses (35%) as compared to those with less severe limitations(15%)
Out of the people living with chronic disabilities:
- 13% were dealing with mood swings and psychosis complications like Alzheimer’s, and Dementia
- 12.3 were having problems with psychological development problems
The people who had mild to severe complications(86%)were more prone to deal with a physical condition as compared to those with severe complications(66%)
Out of the number that had mild to moderate limitations:
- 15.9% were dealing with arthritis and similar complications
- 14.9% were dealing with back-related problems
Bottom Line
Disability is a serious issue that affects a huge number of Australians, and the number will possibly double to 5 million by the time it’s 2023.
Additionally, as the current age group grows older, the likelihood of acquiring a chronic disability will increase, which is why the government of Australia needs to assign more resources to support people living with disabilities and train their carers.